Health economics studies how economic principles can be applied to analyzing health care systems and the health care sector. It covers a wide range of topics, from the production and distribution of health care services to the economic evaluation of medical treatments and health policies. Health economics is a relatively new field that emerged in the 1960s in response to the growing demand for health care services and the rising cost of health care. Health economists are interested in understanding how decisions about health and health care are made and how these decisions impact the overall economy. Keep reading to learn more.
How can you work in health economics?
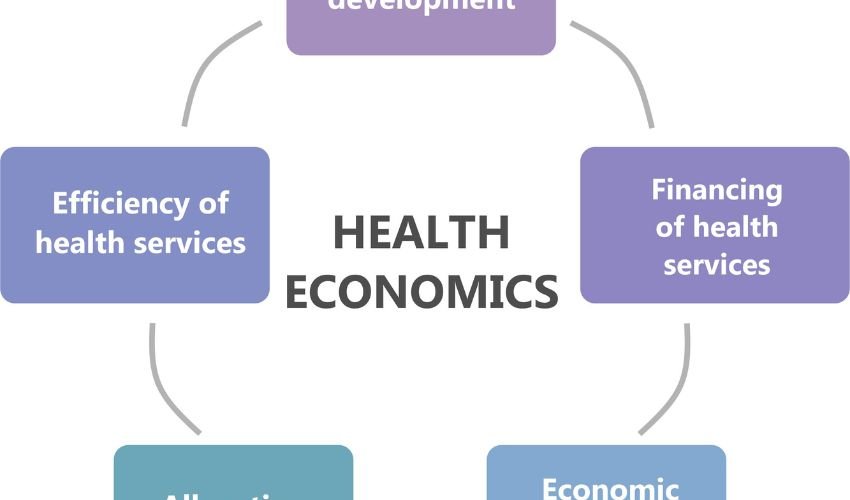
A health economics masters programs teach you how to think about the allocation of scarce health care resources. You learn how to analyze economic factors that affect the supply and demand for health services and apply this knowledge to improve population health. A typical course might cover topics such as:
- The role of markets in the provision of health care
- The impact of government policies on the health sector
- The measurement and valuation of health outcomes
- Health insurance and risk management
- Economic evaluation of medical technologies and treatments
One of the key goals of health economics is to identify ways to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the health care system. This can be done by looking at ways to reduce costs while still maintaining or improving the quality of care. Health economics can also help to identify ways to allocate health care resources more efficiently so that they can be used to provide the most significant benefit to society.
One of the main advantages of health economics is that it provides a framework for thinking about complex health care issues logically and systematically. By taking a holistic approach to the problem, health economists can identify the various factors contributing to the issue and propose possible solutions.
How can health economics be used today?
Health economics includes studying how people pay for health care, how much they are willing to pay, and how those payments affect what care they receive. Health economists also look at the costs of different diseases and injuries and how those costs affect decisions about health care.
Cardiologists in Los Angeles are some of the best in the world. They have access to the latest technology and treatments, allowing them to provide quality patient care. However, cardiology is an expensive field of medicine. The cost of procedures and treatments can be prohibitive for some patients. This can lead to difficult choices for people who need treatment but cannot afford it. Health economics helps us understand these complex issues. By studying how people pay for health care and how that affects what care they receive, we can develop policies that make sure everyone has access to the treatment they need.
How does health economics interact with other fields of study?
Health economics intersects with many other fields of study, including public policy, sociology, and epidemiology.
Public policy is how a government decides what it will do to solve a problem. Health economists help policymakers decide how to spend limited resources on health care. They look at how much health care costs and how different effective treatments are. This information can help policymakers decide whether to fund a new treatment or program or whether to raise taxes to pay for health care.
Sociology is the study of human behavior. Health economists often look at how social factors like income or education level can affect people’s health. For example, they might study how poverty can lead to poor health outcomes. Or they might look at how access to health care affects people’s health.
Epidemiology is the study of diseases and their causes. Health economists sometimes work with epidemiologists to track the spread of illness and figure out ways to prevent it. They may also look at the economic effects of diseases, such as how much money hospitals spend treating patients with illnesses.
Health economics can help to improve health care systems and allocate resources to improve overall health outcomes.